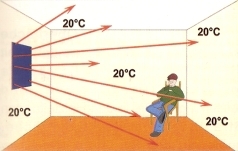
Heat waves emitted by infrared heating panels
The heat given off warms the walls, ceiling, floor, objects and people in the room.
All this collects energy and returns it to the space
The advantage of infrared technology over convection heating
1. Conventional technology (convection heating)
From the above it follows that the traditional conversion of energy into heat is not particularly effective. Nevertheless, conventional heating systems are repeatedly presented by manufacturers and lobbyists as innovative and economical heating technologies. In addition, the essential issues of ongoing maintenance and repair costs for transmission lines as well as chimney cleaning are eliminated.
2. Infrared technology
The big advantage of this technology is that the air is not heated like with conventional convection heaters. All of the energy released by the panels passes through the air without loss and directly heats the walls, people and objects in the room. The operation of the panels can also be compared to the operation of a tiled stove – the principle of heat emission without air and therefore without emission losses.
The walls and objects heated by the heat given off then release the stored heat, thereby achieving a pleasant thermal comfort in the room.
So we are dealing with two types of heat:
a) direct heat given off by the panels
b) indirect heat given off by walls and objects.
This makes the perceived temperature about 2-3 degrees higher than the actual temperature – this saves us energy!
An example of this principle is when we stand in the sun on a hot day and feel the heat rays. However, when we move into the shade, we immediately feel cooler, even though the air temperature in the sun and the shade is actually the same. Thanks to this advantage in a room with a measured temperature of 18°C. The temperature feels like it is around 20 – 21°C. This creates a pleasant indoor climate and saves energy at the same time.
The heat waves emitted dry the walls, improve their insulating properties (a dry wall insulates better than a damp wall) and thus reduce the heat requirement. At the same time, it prevents mold and fungus infestation on the walls.
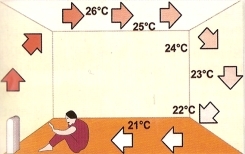
Convection heat
Heat floats in the air according to the principle of air circulation in the room. As a result, the upper layer of space is heated more than the lower one. An unpleasant feeling arises from cold feet and a hot head. The circulation stirs up dust, which leads to the circulation of bacteria in the air.